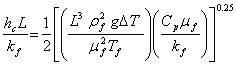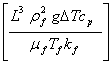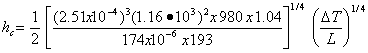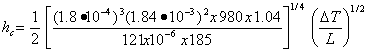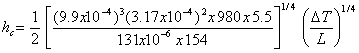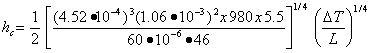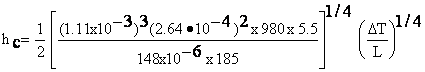|
Physics Division |
|
|
|
|
|
APPENDIX 2a: CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFERThe convective heat transfer coefficient, hc, is given by (from Heat Transmission, W. H. McAdams, McGraw-Hill, NY (1942) pp 242-245):
or where k = thermal conductivity, ρ = density, Cp = specific heat, μ = viscosity, g = gravitational acceleration. Note that CGS units are used. The subscript f means the quantities are to be evaluated at the “gas film” temperature, the arithmetic means of the temperature at the surface of the solid, and the temperature of the bulk of the gas. The quantity L is the characteristic dimension of the system: e.g. diameter of a cylinder, spacing of parallel plates, or the edge length of a plane square. Equation (1) is valid so long as The actual heat flow Q is given by: Q = hc ∆T Watts/cm2
We evaluate expression (1) for several gases and conditions (using CGS units): I. Nitrogen at 293 K and 1 ATM kf = 2.5x10-4 w/cm K, ρf = 1.16x10-3, Cp = 1.04 J/gm K, and μf = 17.4x10-6 poise, so that = 4.04x10-4 II. Nitrogen from 77 K to 293 K (Tf = 185 K, ∆T = 216 K) kf = 1.8x10-4
W/cm K, ρf = 1.84x10-3,
μf = 121x10-6 and = 4.89x10-4
III. Helium from 15 K to 293 K (Tf = 154, ∆T = 278) kf = 9.9x10-4 W/cm K, ρf = 3.17x10-4, Cp = 5.5 J/gm K, μf = 131x10-6 poise, so that = 1.13 x10-3
IV. Helium from 15 K to 77 K (Tf = 46 K, ∆T = 26 K) kf = 4.52x10-4 W/cm K, ρf = 1.06x10-3, μf = 60x10-6 poise, thus = 1.89x10-3
V. Helium from 77 K to 293 K (Tf = 185, ∆T = 216) kf = 1.11x10-3 W/cm K, ρf = 2.64x10-4, Cp = 5.5 J/gm K, μf = 148x10-6 poise
= 1.04x10-3
|